Radiology technicians play a crucial role in healthcare by capturing medical images using X-ray and MRI technology to diagnose conditions. Aspiring radiology technicians must understand how to get radiologic certification, which is required in many states to operate certain imaging equipment and perform specialized exams. While state requirements can vary, most regions require at least an associate degree or equivalent certification to practice. In this guide, we’ll explore how to get radiologic certification, the necessary training, and the best radiology technician schools to help you start your career in this essential healthcare field.
Components of A Successful Radiology Technician Career
Radiology technicians often work long hours and may need to move frequently or stand for extended periods. Their role involves physically assisting patients and providing emotional support during imaging procedures. Precision and attention to detail are essential in this field, especially when reporting results accurately. While it can be a physically demanding job, becoming a radiology technician is a rewarding career, offering the opportunity to serve others in a vital healthcare capacity. If you're interested in pursuing this fulfilling profession, understanding the physical and emotional aspects of the job is important for success.
Continuing education: Radiology Technicians must keep up with the latest innovations and changes in treatment protocols. They must always act in the patient’s best interest and provide safe and effective use of x-ray and other imaging machinery.
Time management: The technical capacity for diagnosis can be a scarce resource particularly in high demand locations like hospital emergency rooms. The x-ray and other diagnostics are essential to proper diagnosis for many patients and medical conditions. Time management is essential for prompt patient care.
Communication skills: Technicians must communicate clearly both in written forms like medical notes and in oral form as they make reports and get instructions. Patients need reassurance as well as technical information about their procedures.
Empathy: Radiology technicians must often work with patients that have illness, disease, or pain. These conditions cause physical and emotional stress. The technician must be aware of these factors and attempt to understand the patient’s needs.
Featured Online Programs
What Does a Radiology Tech Do?
- Complete High school or GED with some coursework in math and science.
- Select an accredited vocational school, community college, or college to study radiology.
- Complete an associate degree in radiology.
- Get experience both as a student and as a graduate; internships or other similar placements will provide a basis of hands-on experience.
- Get a job as a radiology technician.
- Get an online bachelor’s degree in radiology. The online bachelor’s degree is the full entry educational requirement for radiology fields including technician, radiology assistant, radiology technologist.
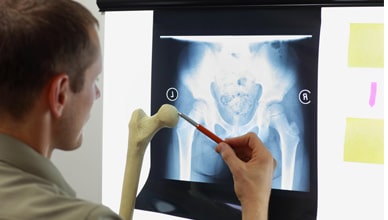 A radiology technician works with patients and radiograph machines. The technician helps produce clear and precise images for use by medical doctors and other medical professionals. In a hospital or clinic settings, the radiologist technicians work directly with patients. The technician can explain the procedure to the patient and the steps needed for an accurate image. The technician must make the patient feel safe and protected in the use of radiation and must position the patient to achieve precise and clear images.
A radiology technician works with patients and radiograph machines. The technician helps produce clear and precise images for use by medical doctors and other medical professionals. In a hospital or clinic settings, the radiologist technicians work directly with patients. The technician can explain the procedure to the patient and the steps needed for an accurate image. The technician must make the patient feel safe and protected in the use of radiation and must position the patient to achieve precise and clear images.
High school students seeking to prepare for college or trade school education in radiology should take science, computer, and math courses. Technician students will benefit from taking classes in math, biology, chemistry, and physics.
Typical Certifications Needed
Radiology technologists need professional certifications, and, in most states, they must have a license. Radiology technicians do not need a certification or a license. Students can use the technician certificate to demonstrate skills and knowledge. The certification program is a faster way to qualify than a two-year degree. Schools offer certifications in a wide range of costs and the time required can range from 6-18 months.
Find Your Online Health Science Program
Academic Standards for a Degree or Certification
The certification process is a faster way to enter the radiology technician field. Students can complete the typical certificate program in about one year. Students still benefit from a period of internship or other hands-on supervised practice. The Associate of Science in radiology is a two-year degree program that consists of approximately 60-70 credit hours. The online bachelor’s level radiology technician degree is a four-year degree that involves general education, radiology training, and internships. Many bachelor level courses offer some opportunity for a focus in one or more areas of radiology practice.
Exams and Experience Needed
There are no formal national exams for radiology technician positions. Most employers require some formal education including a certificate, a two-year degree, or a four-year bachelor’s degree. Master’s level study usually focuses on one or more area of advanced technologists’ practice such as oncology, nuclear medicine, or diagnostic medical sonography.
Radiology Technician Degree & Certification Options
University Headquarters recommends a careful review of options for education in the radiology technician field. While a certificate may offer a quicker path, the rewards in salary and career mobility of an associate or bachelor’s degree may add value to your educational investment. The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists offers meaningful certifications at all levels of radiology practice.
Typical Certificate Coursework for Radiology occupations:
- Anatomy
- Pathology
- Patient Care
- Medical Ethics
- Radiation Physics and Protection
- Image Evaluation
Typical Associate and Bachelor’s coursework for Radiology Occupations:
- Anatomy
- Biology
- Radiology Theory
- Chemistry
- Mathematics
- Patient Positioning
- Patient Safety
Specialized courses:
- Pathology
- Radiation Physics
- Medical Ethics.
Primary Types of Radiology Technician Programs:
- Radiologists are technician level professionals that states qualify by education, testing, and certifications. They work in various specialties like oncology, sonography, and diagnostics.
- Radiology Technologists / Radiographer are terms that describe a technologist level radiology professional. A bachelor’s degree is the usual educational qualification along with certification by the ARRT.
- Radiology Technicians are machine operator professionals that can have a certificate, associate degree, or bachelor’s degree qualification. With higher education, they get higher pay, more responsibility, and a wider range of permitted practice.
- Ultrasound Technicians / Diagnostic Medical Sonographers are specialized machine operators that use sonograph enhanced imagery. This specialization requires certification and licensing in most states. The entry-level education is an associate degree, and a bachelor’s degree is the most common qualification with ARRT certification.
- MRI Technician Is a specialized type of field that uses magnetic resonance technology for internal imaging. This requires ARRT certification plus an associate or bachelor’s degree. Most states license this field and require continuing education.
- CT Tech / CAT Scan Technologist / CT Scan Technologist - Schools, universities, and community colleges offer certificate and associate degree programs in Computer Tomography and Computer Axial Tomography. Some courses limit applicants to licensed radiographers or radiology technologists.
Educational Costs
| Occupation | Certificate | Associate Degree |
|---|---|---|
| CT Tech | $1,500-$10,000 | $5,000-$20,000 |
| *CAT Scan Technologist ** | $1,000-$10,000 | $5,000-$20,000 |
| *CT Scan Technologist ** | $1,000-$10,000 | $5,000-$20,000 |
* ARRT Exam and Certification costs for technologist certificates include application fee of $200.00
** States license Technologist in full or limited authority to practice in the field, many states use the ARRT exams to qualify applicants.
Find Online Health Science Programs
Potential Careers & Salaries for Radiology Technician Graduates
Certificate programs offer a fast way to enter a radiology technician field. Technologists use certifications to enhance their education and skillset by adding new areas of practice. Radiology technicians that graduate from two-year institutions can apply all or part of their community college work towards a bachelor’s degree. They can qualify as technologists and gain substantially higher pay and a wider scope of practice.
Median Salaries by Occupation
| Occupation | Entry-Level | Mid-Career | Late-Career |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist | $300,200 | $358,500 | $375,000 |
| Radiology Technologists or Radiographer | $41,609 | $50,000 | $60,600 |
| Radiology Technicians | $45,600 | $51,700 | $59,500 |
| Ultrasound Technician or Diagnostic Medical Sonographer | $50,183 | $62,000 | $69,000 |
| MRI Technologist | $55,800 | $71,800 | $81,000 |
| CT Tech | $50,500 | $65,200 | $69,300 |
| CAT Scan Technologist | $57,000 | $67,400 | $69,300 |
| CT Scan Technologist | $55,000 | $67,900 | $78,600 |
Important Questions to Ask
How long does it take to earn a degree or certification?
A certificate program usually takes about one year. The range of available certificate programs runs from as little as six months to about one year. The online associate degree for radiology technicians takes about two years and usually includes some period of hands-on training in a hospital, clinic, or another healthcare setting.
How much does a degree or certificate cost?
The costs of education depend on the degree or certificate and the school. Each institution sets the prices for their classes typically at a set fee per credit hour. Across the US there is a wide range of costs. The one-year certificate at an accredited school will range between $3,500 and $10,000; there may be a few schools with lower costs and a few with higher costs.
How many students graduate “on time,” in 12 months or 24 months?
Across the US, the distinct trend is towards longer attendance and not graduating on time. There are significant numbers of students that finish four-year programs in six years and two-year programs in three or more years. Many students attend part-time or take reduced course loads, and these situations cause longer attendance time frames. According to the NCES, the overall graduation rate for Associate degrees was 30% at the three-year mark.
What kind of accreditation does the online program hold? How is it regarded in the field?
University Headquarters recommends that students research their options to find accredited programs for the study of radiology technology. This advice applies to all levels of education including the associate degree, bachelor’s degree, and master’s degree. The Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT) is the leading accreditation agency.
Find Online Health Science Schools
Available Scholarships
-
GMiS Scholarship Program
Amount: U$500-$10,000
Deadline: April 30
The GMiS scholarship supports Hispanic heritage students and other under-represented group members. Applicants may qualify by demonstrating significant contributions to an underserved community. The award selects students that seek higher education in science, technology, mathematics, or a health-related field. Applicants must have a 3.0-grade point average or higher on a four-point scale. Recipients may be enrolled at a two-year or four-year institution; graduate students are eligible. Recipients must attend or plan to attend an accredited US-based college or university.
-
ExxonMobil Bernard Harris Math and Science Scholarships
Amount: $5,000 (4 Awards)
Deadline: Varies (Previously April 8)
This scholarship program awards two scholarships to students of Hispanic descent and two awards to African American students. Applicants must be graduating seniors at a participating school district. The award supports students intending to enroll at a four-year accredited college or university. The applicants must commit to pursuing a STEM field; that definition includes healthcare technology. The selection criteria include academic achievement, leadership, and contributions to their communities.
-
United Health Foundation Louis Stokes Scholarship
Amount: $5,000-$10,000 (4 Awards; renewable up to 4 years)
Deadline: March 31
Named for the founder of the Congressional Black Caucus, the Louis Stokes scholarship award supports African American students seeking to enter health fields. Applicants must be enrolled at an accredited US college or university with a minimum 3.0-grade point average on a four-point scale. Applicants must pursue a degree in a health-related field, and the field of radiology qualifies. Applicants must be US citizens or have permanent residency
-
Two Ten Higher Education Scholarship
Amount: up to $4,000
Deadline: Varies (Previously April 4)
This is a needs-based scholarship intended for students or families with a work history in the footwear industry. Students must be enrolled or intend to enroll in a college, university, two-year college, or vocational school. Students must have and maintain a 2.5-grade point average or higher. The selection criteria include financial need, character, and academic performance.
Professional Organizations
- ASRT
- SMRT
- ACR

ASRT
American Society of Radiologic Technologists
The ASRT involves the entire radiology technology field. This includes radiologists and radiologist assistants. Many radiology technicians aspire to the technologist assistant and technologist levels. This membership organization offers continuing education, news, and research opportunities. The association promotes professional standards and advocates for the profession and for policies that improve healthcare access.

SMRT
Society for Magnetic Radiographers and Technologists SMRT
This international society promotes magnetic resonance and radiographic technology. Radiologic technicians that wish to learn more about radiography and MRI practice can get access to education, information, and job opportunities.

ACR
American College of Radiology
Students and technicians can join the College as allied health members. The association offers information, education, and analysis of trends, changes, and emerging technology. The College has resources for continuing education and advocacy for the profession including safety and working conditions. For technicians that aspire to become radiologists or engage in other occupations in the related technology fields, the College can offer education, insights, and information.
Choosing an Accredited School
University Headquarters recommends The Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT) as the source of accreditation for radiology programs. The JRCERT is a U.S. Department of Education approved agency for radiology programs accreditation. The JRCERT list of accredited vocational schools, colleges, and universities is an excellent approach to finding accredited radiology technician training and education.
Federal student funding is a further advantage of attending an accredited school. The US Department of Education supports student financial assistance programs at accredited institutions. Accreditation by a DOE-approved agency opens the door for federal student loans, grants, and scholarships.
Online vs. On-Campus vs. Hybrid
Today, students seeking an online associate or bachelor’s degree in radiology can attend on-campus, online, or a mix of both types. Online education is accessible to millions of people that cannot or prefer not to participate in classes on a traditional school or college setting. Online education is flexible and typically more affordable than community college or traditional four-year, on-campus education.
Additional Questions
Does the Vocational School Have Post Graduate Job Placement Assistance?
University Headquarters rates post-graduate job placement assistance as an essential part of a comprehensive education program. Vocational education must prepare students to enter the workforce in their area of training. The school has an ideal position to assess the student and promote their efforts for early career development.
Why You Need to Consider the Overall National Rankings of the School and The Effects on Your Career or Salary
School rankings affect salary and career advancements because they can expand the range of job choices for the graduate. School ranking reflects things that concern employers. For example, many school rankings consider graduation rates, retention rates, and the average salary of recent graduates. Employers wish to see schools that take carefully select students, have low drop-out rates, and send graduates off to high paying jobs. To employers, these are signs of high-quality education.
When graduates have a wide range of job choices, they can select high-pay and satisfying jobs. When employers have expectations that graduates can meet their expectations, they extend attractive offers. The overall rankings of a school impact the careers and job choices of recent grads.
Search All Programs
